Lit-Control®
The most advanced, comprehensive and effective medical treatment for Kidney Stones.
Lit-Control® is a revolutionary medical treatment for Kidney Stones combining the most recent scientific advances in nutritional therapy with digital technologies.
Lit-Control® is a family of four innovative medical foods that have been formulated to treat and manage the nutritional needs of patients with each of the four major groups of Kidney Stones (i.e. calcium, uric acid, infectious and cytine stones). And in combination with these medical foods, Lit-Control also incorporates a ground-breaking digital therapeutic to ease the follow-up of these patients.

LIT-CONTROL PRODUCTS
Lit-Control® pH Up
Lit-Control® pH Up is an innovative medical food intended for the treatment of patients with uric acid stones. This product, patent protected and clinically proven, combines two mechanism of actions; the increase of the urine pH because of the magnesium-potassium-citrate, and the inhibition of uric acid crystallization because of the theobromine.
Lit-Control® pH Down
Lit-Control® pH Down is an innovative medical food intended for the treatment of patients with infectious stones. This product, patent protected and clinically proven, reduce the formation of infectious stones such as struvite, carbonate apatite and brushite, through the acidification of the urine with L-methionine.
Lit-Control® pH Balance
Lit-Control® pH Balance is an innovative medical food intended for the treatment of patients with calcium stones. This product, patent protected and clinically proven, reduce the formation of calcium stones such as calcium oxalate and calcium phosphate, through the inhibition of the calcium salts crystallization with phytate, the complexation of the urinary oxalate with magnesium, and the protection of the papillary damage with antioxidants.
Lit-Control® Smart Bottle
Lit-Control® Smart Bottle is a smart bottle that measures your water consumption throughout the day to help you to be hydrated. Lit-Control® SmartBottle connects by Bluetooth® to an App that allows you to keep track, set goals and check your progress. It is compatible with iOS and Android smartphones.
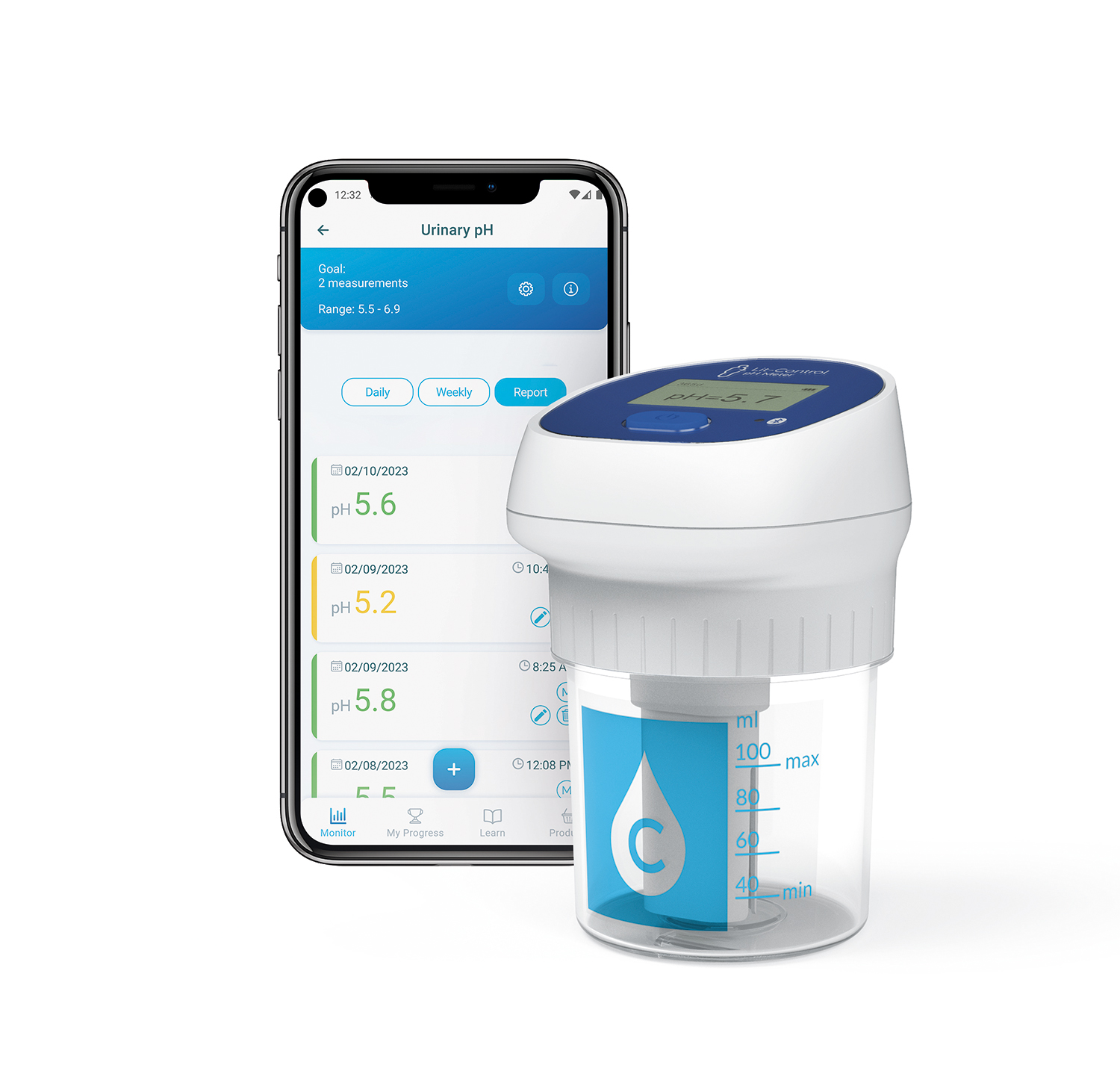
Lit-Control® pH Meter
Lit-Control® pH Meter is an innovative first-in-class medical device intended to measure the urine pH of stone-formers with excellent outcomes in terms of sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value (PPV), negative predictive value (NPV) and accuracy. This product, patent protected and clinically proven, is the best option to measure the pH in a fresh urine (just after the urination) to take quick and reliable clinical decisions in the doctor's office, or to monitor the patient's urine pH during the day (circadian rhythms) easily and conveniently at home.
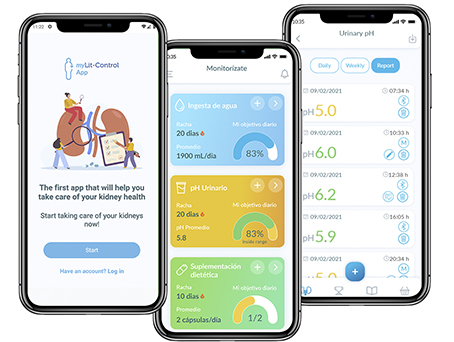
myLit-Control APP
Easily track your kidney health by daily measuring water intake, urinary pH, and food supplement intake. Complete your daily monitoring goals and continue working towards kidney stone prevention!
Easy synchronization with Lit-Control® pH Meter 2.0 and Lit-Control® Smart Bottle. Automatically transfer your data to the app via Bluetooth.®
SPECIFIC STRENGTHS OF LIT-CONTROL®
Patent protected
Clinically proven